Let’s start by understanding Boosting! Boosting is a method of converting weak learners into strong learners.
Category: Uncategorized
Logistic Regression Case Study
“ Logistic Regression measures the relationship between the categorical dependent variable and one or more independent variables by estimating probabilities using a logistic function. “
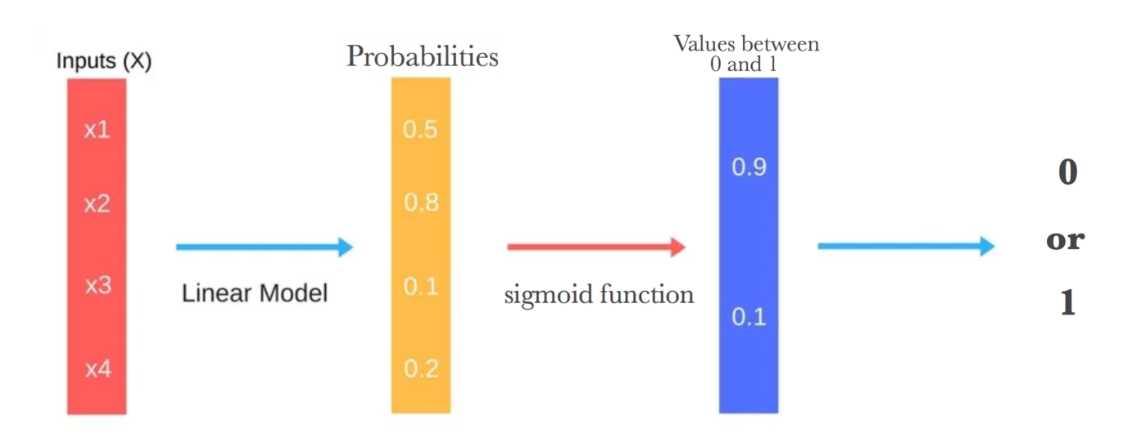
Table of Contents
- What is Logistic Regression ?
- Why not Linear Regression ?
- How does Logistic Regression work ?
- Decision Boundary
- How to check model performance ?
- Summary
What is Logistic Regression ?
You already know that linear regression is used to predict continuous Y variables.
In linear regression the Y variable is always a continuous variable. If suppose, the Y variable was categorical, you cannot use linear regression model it.
So what would you do when the Y is a categorical variable with 2 classes?
Logistic regression can be used to model and solve such problems, also called as binary classification problems.
A key point to note here is that Y can have 2 classes only and not more than that. If Y has more than 2 classes, it would become a multi class classification and you can no longer use the vanilla logistic regression for that.
Another advantage of logistic regression is that it computes a prediction probability score of an event. More on that when you actually start building the models.
Why not Linear Regression ?
How the random forest algorithm works ?

Introduction to Random Forest Algorithm
In this article you are going to learn the most popular classification algorithm , Random Forest. To motivate you further about this algorithm , I will tell you the best advantages of using Random Forest Algorithm.
Random forest algorithm can be worked both for classification and regression problems. It is one of the most accurate learning algorithms available. For many data sets, it produces a highly accurate classifier. It runs efficiently on large databases.
Table of Contents :
- Approach of Random Forest Algorithm
- Difference between Decision Trees and Random Forests
- How Random Forest Algorithm Works
- Important Hyperparameters
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Summary
Before getting into the technical part of algorithm , let’s understand the random forest algorithm in layman language.
Suppose Edward decides to go on a vacation for a week with his family. He wants to visit a place where he and his family can enjoy the most.
So he asks his best friend , Mathew to suggest him good places. Then his friend started asking Edward about his interests , past trips , liking towards adventure , night life or nature.
Mathew recommended Edward the best place to visit for vacation based on the answers given by him. Basically , he formed the decision tree with the answers given by Edward.
As his best friend may recommend his best place to Mathew as a friend. The model will be biased with the closeness of their friendship. So he decided to ask few more friends to recommend the best place he may like.
Now his friends asked some random questions and each one recommended one place to Edward. Now Mady considered the place which is high votes from his friends as the final place to visit.
We have already discussed basic approach of two algorithms Decision Tree and Random Forest by now. Let’s understand the difference between the Decision Tree and Random Forest Algorithm more deeply.
Difference between Decision Trees and Random Forests
Decision Tree is a supervised, non parametric machine learning algorithm. Used for both classification as well as regression problems.
It is a graphical representation of tree like structure with all possible solutions. It helps to reach a decision based on certain conditions.
Random forest is the most simple and widely used algorithm. Used for both classification and regression. It is an ensemble of randomized decision trees. Each decision tree gives a vote for the prediction of target variable. Random forest choses the prediction that gets the most vote.
An ensemble learning model aggregates multiple machine learning models to give a better performance. In random forest we use multiple random decision trees for a better accuracy.
How Random Forest Algorithm Works
- Randomly select “k” features from total “m” features.
- Where k << m
- Among the “k” features, calculate the node “d” using the best split point.
- Split the node into daughter nodes using the best split.
- Repeat 1 to 3 steps until “l” number of nodes has been reached.
- Build forest by repeating steps 1 to 4 for “n” number times to create “n” number of trees.
Out of Bag Error :
For each bootstrap sample, there is one third of data which was not used in the creation of the tree, i.e., it was out of the sample. This data is referred to as out of bag data. In order to get an unbiased measure of the accuracy of the model over test data, out of bag error is used. The out of bag data is passed for each tree and the outputs are aggregated to give out of bag error. This percentage error is quite effective in estimating the error in the testing set and does not require further cross validation.
Important Hyperparameters
Hyperparameters are used to tune the model and make it faster providing better accuracy.
I will here talk about the hyperparameters of sklearns built-in random forest function.
Firstly, there is the „n_estimators“ hyperparameter, which is just the number of trees the algorithm builds before taking the maximum voting or taking averages of predictions. In general, a higher number of trees increases the performance and makes the predictions more stable, but it also slows down the computation.
Another important hyperparameter is „max_features“, which is the maximum number of features Random Forest considers to split a node.
The last important hyper-parameter we will talk about in terms of speed, is „min_sample_leaf “. This determines, like its name already says, the minimum number of leafs that are required to split an internal node.
The „n_jobs“ hyperparameter tells the engine how many processors it is allowed to use. If it has a value of 1, it can only use one processor. A value of “-1” means that there is no limit.
„random_state“ makes the model’s output replicable. The model will always produce the same results when it has a definite value of random_state and if it has been given the same hyperparameters and the same training data.
Lastly, there is the „oob_score“ (also called oob sampling), which is a random forest cross validation method. In this sampling, about one-third of the data is not used to train the model and can be used to evaluate its performance. These samples are called the out of bag samples. It is very similar to the leave-one-out cross-validation method, but almost no additional computational burden goes along with it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Random Forest
Advantages of Random Forest
- High predictive accuracy.
- Efficient on large datasets
- Ability to handle multiple input features without need for feature deletion
- Prediction is based on input features considered important for classification.
- Works well with missing data still giving a better predictive accuracy
Disadvantages of random forest
- Not easily interpretable
- Random forest overfit with noisy classification or regression
The Journey Begins
Thanks for joining me!
Good company in a journey makes the way seem shorter. — Izaak Walton

